- SR Flip-Flop (Set Reset)
- D Flip-Flop (Data)
- JK Flip-Flop
- T Flip-Flop (Toggle)
Those Flip-Flops are available in market in IC Package Form. Now You have a circuit that uses 1 JK and 1 D Flip-Flop and 3 NOT Gates. So you have to buy three ICs- one for JK, one for D and other for NOT Gate. Ultimately you will see that a flip flop in IC of JK, a flip-flop in D IC and 3 NOT gates are not used. Now, if you convert a JK flip flop into D flip flop then you didn’t have to pay for the D flip flop IC. So, your circuit will be made by 2 ICs in place of 3 and in cheap cost. This article is for that reason. How the Flip-Flops are converted from one to other.
Procedure: 1. Write Qt and Qt+1 Table with 4 combination of 0 and 1. 2. Write columns for inputs of destination Flop-Flop. 3. Write the cell values depending on the Q Table’s State. (i.e., For what input in this flip flop the out put will be that under Qt and Qt+1. 4. Now Draw column(s) for input of source flip flop. 5. Fill the Cells as before. 6. Now, consider one input of source flip flop as an output. And then take Q and input(s) of destination flip flop to make a K-Map. 7. Work out the expression for this input of the source flip flop. 8. Now, consider the other input (if there is two inputs) of source flip flop as output and do the same as point 6 and 7. 9. Now make the circuit for those Expressions and join them. 10. Now the input(s) of your circuit will be the input(s) of your destination Flip-Flop.
From SR To Other

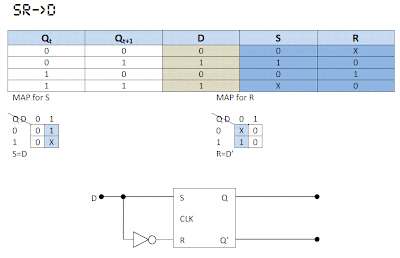








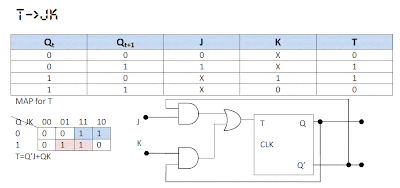

Comments